Detail Overview of Humour Exercises
The Class 12 English chapter on Humour seeks to address the psychology and social relevance of the laughter. According to the findings by Sophie Scott, it underlines the idea that laughter is not only a response to something funny; it is simply an indispensable means of emotional communication and stress alleviation. However, funnily enough, most laughter is not evoked by humour instead it is caused by social interaction by action usually in order to relieve tension and get in touch with the other person.
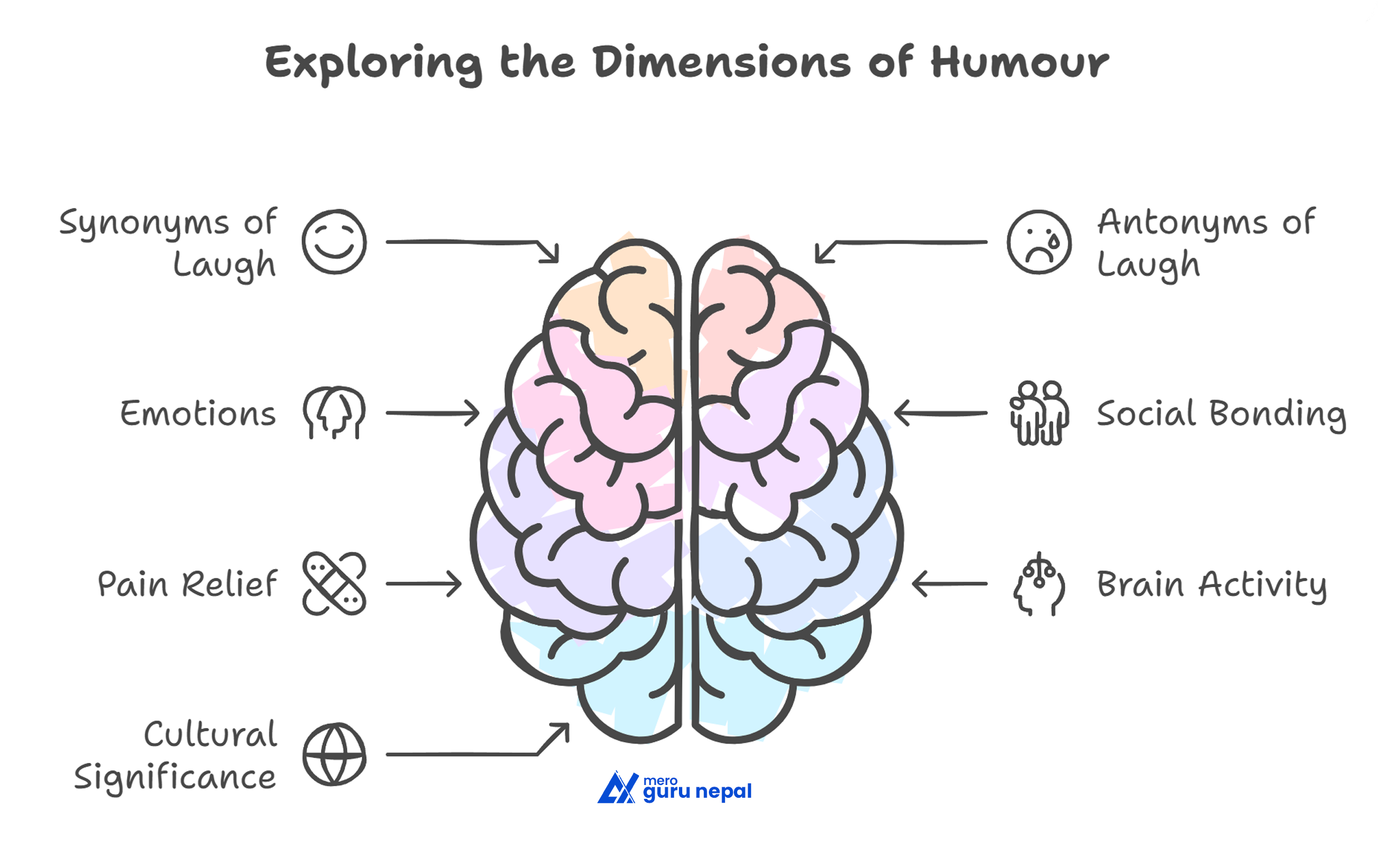
The chapter contains a vocabulary practice on the topic of development of synonyms and antonyms of the verb laugh, definitions of such common emotions as happiness, disgust, and triumph, and comprehension activities based on the study by Scott. It highlights the fact that, laughter is contagious, affected by a group environment and even serves as a natural painkiller which involves the release of endorphins.
In the critical thinking, the students are made to critique on the essence of laughing together as a couple as well as value of crying. The composing assignment prompts a perceptual account of one of the favorite comedians- the heritage of Charlie Chaplin. The grammar exercises teach the learners how to apply frequency adverbs in their everyday utterances.
On the whole, this chapter relates humour to human psychology, relationships, emotional healing and communication.


Continue reading the ‘Humour Exercises’ in meroguru app









Summary of Humour Exercises
The chapter Humour explores the science and social significance of laughter. It presents findings from neuroscientist Sophie Scott, who explains that laughter is a complex, universal human behavior that often has more to do with social bonding than humor itself. Through studies across cultures, it’s shown that laughter is contagious, meaningful, and vital for relationships, acting as a painkiller and a stress reliever. The chapter also dives into emotions related to laughter, contrasts humor with other emotional responses, and discusses how laughter plays an important role in communication, even among couples and in public performances like stand-up comedy. Exercises reinforce vocabulary, emotional understanding, grammar (adverbs of frequency), and personal reflection through writing.
Key Takeaways of Humour Exercises
- Laughter is universal and one of the most misunderstood behaviors.
- It serves social bonding purposes rather than always being about humor.
- Couples who laugh together tend to have longer-lasting relationships.
- Laughter acts as a painkiller, thanks to the release of endorphins.
- People may laugh or giggle during pain or awkwardness as a coping mechanism.
- Laughter is contagious, especially in crowds, which comedians use to their advantage.
- Babies and adults alike share two emotional expressions: crying and laughter.
- Emotional expressions like fear, anger, disgust, happiness, sadness, surprise, relief, and triumph have specific definitions and social roles.
- Grammar focus: frequency adverbs like “often,” “sometimes,” and “never.”
- Writing tasks explore personal reflection, like describing a favorite comedian (e.g., Charlie Chaplin).
FAQ:
Why do people sometimes laugh during painful or awkward situations?
They may laugh to reassure themselves and others that they are okay or to ease emotional discomfort.
What did Sophie Scott discover through her study in Namibia?
She found that laughter is one of the most important and rich vocal behaviors humans use.
How is laughter used in social bonding?
Laughter brings people together and strengthens relationships, even without something being overtly funny.
How does laughter benefit romantic relationships?
It helps reduce tension and contributes to emotional connection and longer-lasting bonds.
In what way does laughter act like a painkiller?
Laughter increases pain thresholds by triggering the release of endorphins, which are natural pain relievers.
What part of the brain is involved in responding to laughter?
The brain’s mirror regions, which mimic others’ actions, are activated during laughter.
Which emotions are considered universal?
Fear, anger, surprise, disgust, sadness, happiness, relief, and triumph.
How do comedians benefit from crowd laughter?
The contagious nature of laughter in a crowd amplifies their performance and helps them connect with the audience.
What is meant by “there is always a meaning to it” in regard to laughter?
Laughter is never truly neutral; it always reflects an emotional or social context.
How is Charlie Chaplin an example of timeless humor?
Through his character “The Tramp,” Chaplin used silent comedy and relatable struggles to connect universally with audiences, often combining humor with emotion.
Leave a Reply