Detail Overview of Money and Economy Exercise
Content





Continue reading the ‘Money and Economy Exercise’ in meroguru app











Summary of Money and Economy Exercise
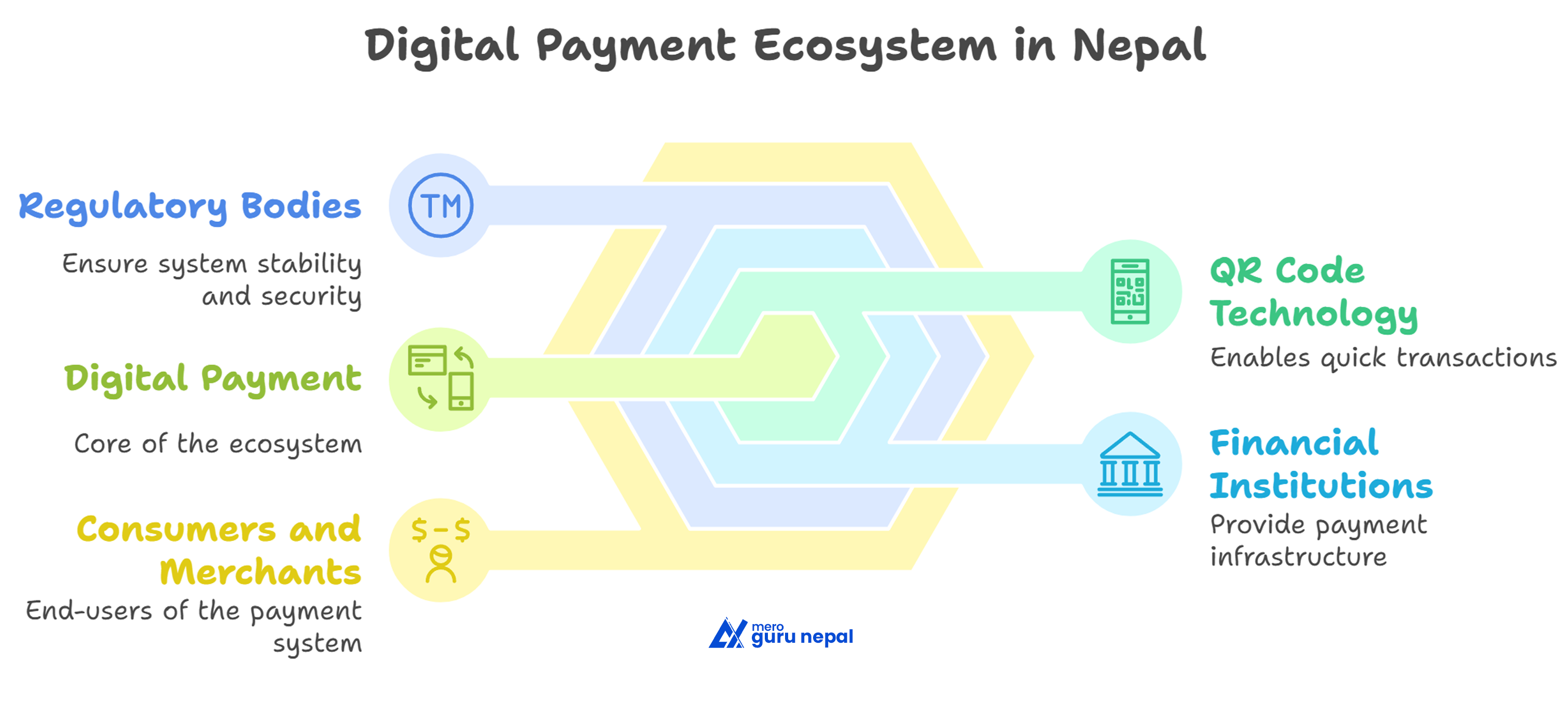
The chapter Money and Economy from Class 12 English focuses on the increasing relevance of digital payment systems, especially QR code-based transactions. It highlights how tech giants like Tencent and Alibaba initially utilized QR codes and how global companies like Visa and Mastercard adopted the system to improve payment security and efficiency. The lesson explains the role of scheme operators, potential risks, and the need for consumer awareness in digital transactions. It also reflects on Nepal’s growing adoption of QR payments, addressing challenges such as infrastructure, awareness, and interoperability in its digital economy transition.
Key Takeaways
- QR codes are transforming how people make payments globally.
- Companies like Tencent and Alibaba were pioneers in using QR codes.
- Nepal is slowly embracing QR code payments, especially post-Covid.
- Digital payments can bring transparency and efficiency to the economy.
- Government and private collaboration is essential for a stable digital payment ecosystem.
- Consumer awareness and internet accessibility are critical for growth.
- Scheme operators help standardize and secure QR payment systems.
FAQ:
How do QR code payments work, according to Class 12 English?
QR code payments work by either scanning the merchant’s QR code or presenting one’s own for the merchant to scan, enabling fast and secure transactions.
Why is the QR code system important in the Class 12 English chapter Money and Economy?
It demonstrates how digital payments can revolutionize traditional financial systems, making payments faster, safer, and more accessible.
What companies are mentioned in the Class 12 chapter Money and Economy regarding QR code usage?
Tencent, Alibaba, Visa, and Mastercard are mentioned as key players who integrated QR codes into their platforms for payments and services.
What challenges are discussed in implementing QR payments in Nepal?
The text mentions issues like lack of infrastructure, low awareness, and limited interoperability as barriers to fully adopting QR payments in Nepal.
What does Class 12 English suggest as a solution to QR payment challenges?
It recommends government support, awareness campaigns, better internet access, and collaboration between service providers and financial institutions.
What role does a scheme operator play in QR code systems?
A scheme operator defines rules, manages branding at payment points, and handles disputes, ensuring smooth operation of QR-based systems.
Is QR code payment secure as per the Class 12 Money and Economy chapter?
Yes, the chapter states that QR payments can be secure if merchant IDs, user registration, and real-time payment notifications are implemented.
Can QR code payments help formalize Nepal’s economy?
Yes, the chapter suggests QR codes can transform the informal economy by encouraging digital, traceable transactions.
Why is Money and Economy an important lesson in Class 12 English?
It links language with real-world digital trends, educating students about economic shifts and encouraging digital literacy.
Leave a Reply